
Close

The ERA6 reanalysis, developed by the European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF), marks a significant leap forward in climate and weather data analysis. Building on the foundation of its predecessor, ERA5, ERA6 integrates years of rigorous research and development alongside advancements in computational technology. This new iteration addresses known limitations of ERA5, offering unprecedented detail and reliability in high-resolution climate data. Below, we delve into the key improvements that distinguish ERA6 from ERA5.
One of the standout features of ERA6 is its higher spatial resolution. The horizontal resolution has been refined to 18 km, a substantial improvement over ERA5’s 27 km (equivalent to 0.25 degrees of latitude and longitude). This enhanced resolution enables a better representation of mesoscale phenomena, such as localized weather systems, and improves the coupling between ocean and atmosphere processes.
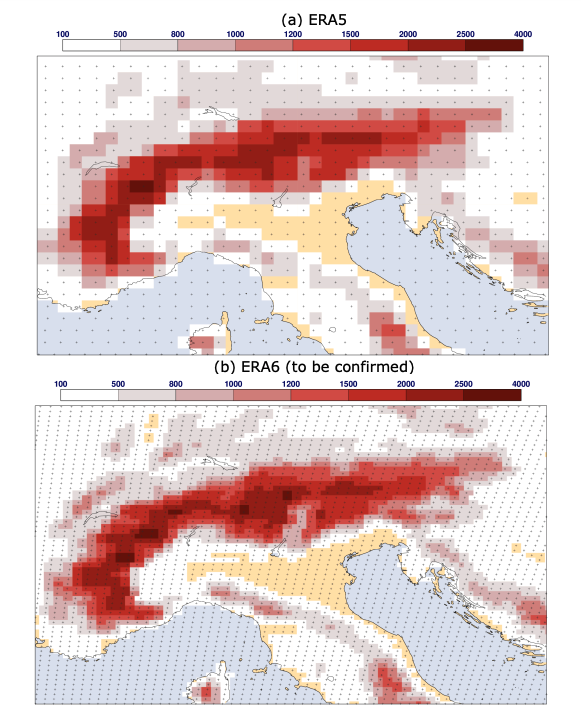
Horizontal grid of ERA5 and ERA6 most likely configuration. Credit: Copernicus Climate Change Service/ECMWF
ERA6 incorporates state-of-the-art four-dimensional variational (4D-Var) data assimilation methods, along with reprocessed observational datasets. These enhancements are specifically designed to reduce known biases, such as the persistent cold temperature biases observed in the lower stratosphere (above 10 hPa) in ERA5. Additionally, significant improvements will be made in snow assimilation and representation.
ERA6 will integrate rescued early satellite data (pre-1979) and reprocessed historical observations (C3S2_310, EUMETSAT, and C3S2_314). Efforts include decoding original archives, correcting geolocation and timing errors, and ensuring high-quality data storage.
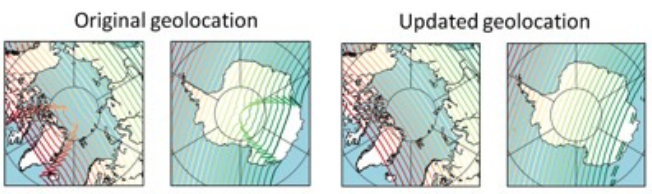
Example of correction for geolocation at the poles in early Nimbus sensors THIR. Credit: Copernicus Climate Change Service/ECMWF
ERA6 introduces significant improvements in near-surface realism and radiative forcing accuracy. This includes updates to dynamic vegetation cover and type, lake properties, urban tiles, and the inclusion of new aerosol species. These enhancements contribute to a more precise depiction of land-atmosphere interactions and the energy balance within the climate system.
ERA6 includes a one-way coupled model for ocean waves, providing a consistent representation of ocean-atmosphere processes. The reanalysis will leverage fields from ORAS6 and OCEAN6, enabling detailed analysis of ocean dynamics, such as surface eastward and northward sea water velocities. This integration is expected to provide a more cohesive understanding of the interplay between marine and atmospheric systems.
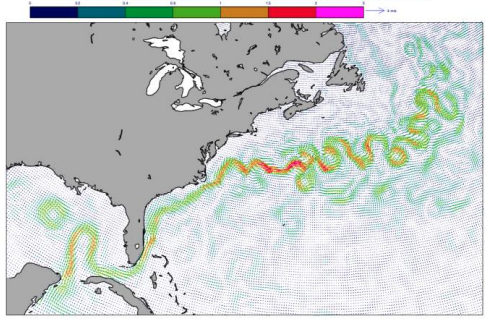
Example of hourly surface Eastward/Northward sea water velocity. Credit: Copernicus Climate Change Service/ECMWF
Modeled wind resource data for the wind industry.
At any site around the world. Onshore and offshore.